NRC Proposal New Steelhead Limits
New Proposal
There is a new proposal up for consideration by the NRC that would reduce Steelhead bag limits on several sections/streams in Michigan. Here is the NRC Proposal New Steelhead Limits being considered by the NRC. The current steelhead management plan for Michigan needs to be revised to reflect current trends, conditions, and annual adult spawning migrations. We are not opposed to people having the opportunity to harvest a fish even though we practice catch and release. This request for change has nothing to do with gear restrictions and by no means should we dictate how people can legally fish for steelhead. Steelhead populations are in decline and have been on the long slide for over the past decade. Which raises several questions and highlights a need to address and discuss the future of Steelhead management in our state.
Data gaps and changing environmental conditions have muddied the waters, but indicators are everywhere. Anyone that has spent any amount of time on the water can see the changes that have occurred. Which poses several questions. What is the current status of spawning steelhead in our streams? Does the current management scheme reflect what anglers are currently experiencing in their catch rates? Can a declining steelhead population survive added angling pressure with todays current harvest allowance? The MDNR has admitted there is a problem, but currently there has been a failure to act even though there are plenty of red flags.
Little Manistee River
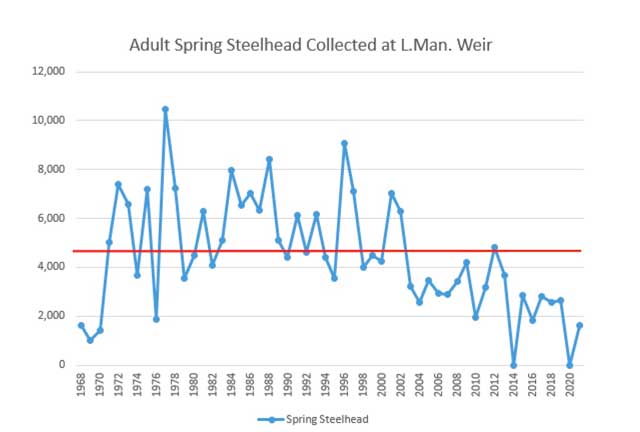
The Little Manistee River Weir boasts the best available data for returning spring Steelhead. This little river is the sister river to the Big Manistee. Albeit smaller in size, it can still shed light on the current trend of Steelhead returns in the Big Manistee River. Since 2002 there has been a significant reduction in Spring Steelhead in the Little Manistee River. The 6 year average from 2009-2014 was 3,433 returning adults and from 2015 to present it was 2,389 returning adults (excludes 2020). In the last 6 years there has been a 30% reduction in average spawning adults. If this trend continues, then what? The spring 2021 returns were the lowest since 1970. More importantly, every year since 2003, the spring steelhead counts have been below the 53 year average of 4,648 adults.
Are we just going to standby and watch our Steelhead populations decline to a point of no return? It’s not far fetched to consider the outcome of 10 more years of decline. The consequences could ultimately exceed the ability of the population to recover. There is a COST TO NO ACTION! Steelhead catch rates are declining statewide as well. Right now this state has a Steelhead catching issue. The proposed rule changes will probably not boost the overall population size, but a declining Steelhead population will not promote productive fishing. This proposal is a good start to a long overdue conversation. Catch Rates, Harvest, and Angler Satisfaction are currently out of balance. We can’t afford to wait for things to get any worse! Now is the time to have a serious discussion regarding harvest limits. What should our annual harvest look like based upon today’s current steelhead population trend? We need to bring the Harvest and Catch Rates back to the middle and rebalance Angler Satisfaction.
Big Manistee River
The close proximity of the Little Manistee River to the Big Manistee River also raises parallel questions. Is there a similar population trend occurring in the Big Manistee River? What about the rest of the Lake Michigan Basin? Is this trend occurring throughout the Great Lakes Region? We believe it is! How can we continue the “Business as Usual” model? To say there isn’t a biological reason to consider a regulation change is a dangerous claim. Just because you have an inherent lack of data doesn’t excuse you from responding to the problem. Changing the regs is a short term fix that will allow more time for data collection. Fully understanding the complexities surrounding the Steelhead population decline will take time. How long will “the data collection” take, 5-10 years? Can we justify waiting that long without taking action? Is it worth risking this popular fishery? Just a little food for thought.
Email NRC
We encourage everyone to email your own letter to the NRC. This is an important issue and if you enjoy fishing for steelhead you should be paying attention. Acting now may avert loosing something that is more than 100 years in the making. Here is the email for the NRC , please send your public comments to this address before November 10th.